HOW TO REGULATE YOUR BLOOD SUGAR NATURALLY
Table of Contents
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
What is Blood Glucose?
So, what exactly is blood glucose? Simply put, it’s the sugar that travels through your bloodstream to give your body energy. When you eat food, your body breaks it down, and a good chunk of that becomes glucose. This glucose then gets absorbed into your blood. Think of it like fuel for your car – your body needs this fuel to function, from your brain thinking to your muscles moving. For most people, the body has a pretty good system for keeping these levels in check. Insulin, a hormone made by your pancreas, acts like a key, letting glucose into your cells. When this system works well, your energy levels stay pretty stable.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar
Lots of things can nudge your blood sugar levels up or down. What you eat is a big one, of course, especially carbohydrates. But it’s not just about food. Stress can really mess with your levels – ever felt jittery and then realized you’re just anxious? That can be your blood sugar acting up. Not getting enough sleep can also throw things off. Even being a little dehydrated can make your blood sugar climb. And if you’re sick or fighting off an infection, your body releases hormones that can raise your blood sugar. It’s a complex dance, really.
Here’s a quick look at some common influences:
- Food Intake: Especially carbohydrates and sugars.
- Physical Activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar.
- Stress Levels: Emotional or physical stress.
- Illness/Infection: Your body’s response to sickness.
- Medications: Certain drugs can affect blood sugar.
- Sleep Quality: Lack of sleep can impact levels.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
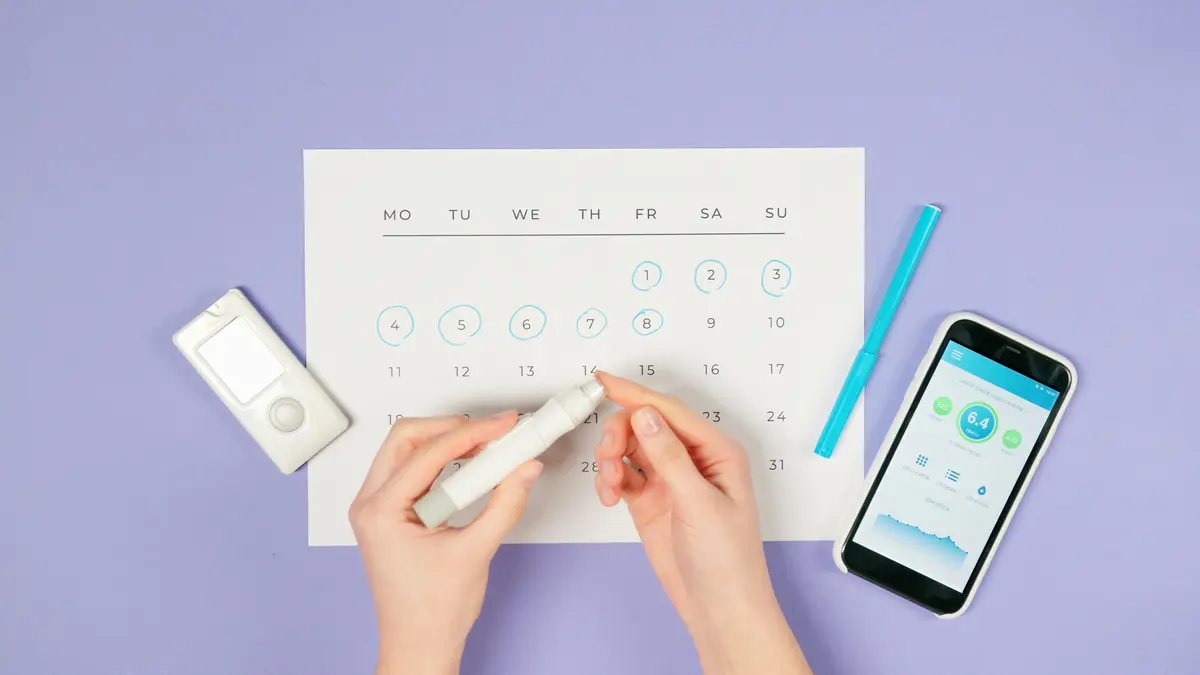
Keeping an eye on your blood sugar is super helpful, especially if you have concerns about your levels. You can do this at home using a blood glucose meter, often called a glucometer. It involves a tiny prick on your finger to get a small blood sample, which you then place on a test strip. The meter reads it and gives you a number. Some people also use continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), which have a small sensor under the skin that checks your sugar every few minutes. It’s a good idea to talk to your doctor or a diabetes educator about how often you should check and what your target numbers should be. They can help you understand what the readings mean for you.
Generally, here are some common times people check their blood sugar:
- First thing in the morning, before eating or drinking.
- Right before a meal.
- About two hours after starting a meal.
- At bedtime.
Checking your blood sugar regularly helps you and your healthcare team understand how different foods, activities, and even your mood affect your levels. This information is key to making smart choices for better health.
Healthy Eating Habits to Support Blood Sugar Balance
When you’re trying to keep your blood sugar in a good spot, what you eat plays a pretty big role. It’s not just about avoiding sweets, though that’s part of it. We’re talking about building meals that work with your body, not against it. Think of it like this: your body breaks down food into sugar for energy, but how quickly that happens can really change things.
The Role of Protein in Blood Sugar Control
Protein is like a traffic cop for sugar. It helps slow down how fast sugar gets into your bloodstream. This means you get a steadier energy release instead of a big spike and then a crash. Aiming for a good amount of protein with your meals can make a real difference. It doesn’t have to be complicated; just try to include sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, or tofu.
Balancing Carbohydrates and Fiber
Carbs are a bit of a mixed bag. They’re our main energy source, but some break down into sugar really fast. That’s where fiber comes in. Fiber acts like a buffer. Foods with lots of fiber, like whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa), vegetables, and fruits, take longer to digest. This delay means the sugar from those carbs enters your blood more gradually. So, pairing your carbs with fiber-rich foods is a smart move.
Here’s a quick look at how fiber helps:
- Slows Digestion: Fiber makes your digestive system work a bit harder, delaying sugar absorption.
- Promotes Fullness: It helps you feel satisfied longer, which can prevent overeating.
- Supports Gut Health: A healthy gut often means better overall metabolic function.
Smart Food Choices for Stable Levels
Making good food choices is all about balance. It’s not about eating perfectly all the time, but about putting together meals that help keep things steady. Combining different food groups is key. For example, instead of just a plain bagel (mostly carbs), try having it with some eggs or avocado. This adds protein and healthy fats, which helps slow down the sugar release from the bagel.
It’s easy to think of food as just fuel, but it’s also about how our bodies process it. When we eat, especially carbs, our body turns them into glucose. The speed at which this glucose enters our blood can cause our levels to jump up or stay more even. Building meals with a mix of protein, fiber, and healthy fats helps manage this process.
Here are some ideas for balanced meals:
- Breakfast: Choose between oatmeal topped with berries and nuts, or scrambled eggs with whole-wheat toast and avocado on the side.
- Lunch: A large salad with grilled chicken or beans, and a light vinaigrette.
- Dinner: Baked salmon paired with roasted vegetables and a modest portion of quinoa.
- Snacks: A handful of almonds, Greek yogurt with a few berries, or apple slices with peanut butter.
How Physical Activity Affects Your Health
Physical activity isn’t just about burning calories or building muscle—it’s one of the easiest ways to help regulate your blood sugar. It doesn’t always have to mean intense workouts, either. Even small bouts of movement, like cleaning out the garage or pacing while you’re on the phone, can make a difference. Let’s break down how movement helps and what you should know about exercise for blood sugar control.
How Exercise Affects Blood Sugar
When you get your body moving, your muscles pull more sugar out of your blood to use as fuel. Over time, regular movement helps your body listen to insulin better, which means better blood sugar control overall.
- Exercise can lower your blood sugar even hours after you finish.
- Intense activities have a longer-lasting effect than light ones.
- It’s normal for your numbers to drop more with new or strenuous routines.
Here’s a quick look at the typical impact of different types of activity:
| Activity Type | Blood Sugar Impact | Duration of Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Brisk Walking | Mild to Moderate | 2–12 hours |
| Cycling or Swimming | Moderate | 6–24 hours |
| Weight Lifting | Moderate | 2–24 hours |
| Housework/Gardening | Mild | 1–6 hours |
Sometimes the toughest step is just getting started. Even a short walk after meals can level out those blood sugar swings.
Incorporating Light and Strenuous Activity
You don’t have to run marathons—mixing up your activities is often easier and more fun:
- Light activities: walking the dog, tidying up, stretching
- Moderate activities: brisk walking, casual cycling, water aerobics
- Strenuous activities: running, intense cycling, lap swimming, circuit training
A good weekly goal? Try for 30 minutes most days, or around 150 minutes a week. Add in muscle-strengthening tasks 2–3 times a week, too.
Tips for getting started:
- Check your blood sugar before and after exercise, especially if you use insulin.
- Carry a small snack in case your sugar dips too low.
- Stay hydrated with water, especially in warmer weather.
Benefits Beyond Blood Sugar Management
Physical activity doesn’t only help with glucose numbers. You might notice:
- Improved mood — those endorphins are real!
- Easier weight management
- More energy for everyday stuff
- Stronger bones and muscles
- Less stress and better sleep
Regular movement can really change the way you feel. It’s not just for managing health problems—it’s about feeling your best day-to-day.
Simple Habits to Promote Blood Sugar Stability
Beyond what you eat and how much you move, there are other daily habits that play a big role in keeping your blood sugar steady. It’s not just about the big stuff; the little things add up, and sometimes they’re the easiest to adjust.
Mindful Eating and Portion Control
Paying attention to what and how much you’re eating is a game-changer. It’s easy to just eat until you’re full, but knowing what a good portion looks like for different foods can make a real difference. Think about it: a serving of meat is roughly the size of a deck of cards, and a serving of cooked pasta or rice is about what fits in your fist. Using measuring cups or a food scale can help at first, just to get a feel for it. This isn’t about strict rules, but more about building awareness so you can make better choices without always having to measure.
The Importance of Hydration
Drinking enough water is surprisingly important for blood sugar. When you’re dehydrated, your blood sugar can actually go up. Water helps your kidneys flush out extra sugar, and staying hydrated can help prevent those spikes. Aim for plain water most of the time. It’s simple, but it works.
Limiting Sugary Drinks and Alcohol
This one’s a biggie. Drinks loaded with sugar, like regular soda, fruit juices, and many sports drinks, can send your blood sugar through the roof very quickly. They often don’t offer much in the way of nutrients either. While a sugary drink can be used in a pinch to quickly raise dangerously low blood sugar, for everyday balance, it’s best to steer clear. Alcohol can also mess with your blood sugar, sometimes causing it to drop, other times to rise, depending on what you’re drinking and how much. It’s best to talk to your doctor about safe alcohol consumption if you have diabetes.
Making small, consistent changes to your daily routines can have a significant impact on your overall health and blood sugar management. It’s about building sustainable habits rather than drastic overhauls.
Key Factors in Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes isn’t just about taking medication; it’s a daily dance with your body’s responses. Understanding how different parts of your routine affect your blood sugar is super important. It’s like learning the rules of a game so you can play it well.
Consistency in Meal Times
Eating at roughly the same times each day can make a big difference. When you eat irregularly, your body doesn’t know what to expect, and this can lead to unpredictable blood sugar spikes and drops. Think of it like this: your body has an internal clock, and regular meals help keep that clock running smoothly. This is especially true if you’re on certain diabetes medications, like insulin, where timing is key to prevent lows or highs.
Understanding Food’s Effect on Sugar
It’s not just what you eat, but how much and what you combine it with. Different foods affect your blood sugar differently. For instance, simple carbs like white bread or sugary drinks cause a quick rise, while meals with protein, healthy fats, and fiber tend to release sugar more slowly. Learning to read food labels and understanding basic nutrition can help you make better choices.
Here’s a quick look at how different food types can impact your blood sugar:
| Food Type | Typical Blood Sugar Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sugary Drinks | Rapid Increase | Best avoided, except for emergencies |
| Refined Grains | Quick to Moderate Increase | Choose whole grains when possible |
| Lean Proteins | Minimal Impact | Helps with satiety and slower digestion |
| Non-Starchy Veggies | Minimal Impact | Packed with nutrients and fiber |
| Healthy Fats | Minimal Impact | Aids in nutrient absorption and fullness |
Tracking Food and Activity
Keeping a log of what you eat and how much you move can be incredibly revealing. It helps you connect the dots between your choices and your blood sugar readings. You might notice that a particular meal consistently leads to a high reading, or that a brisk walk helps bring it down. This kind of personal data is gold for you and your healthcare team.
Keeping track doesn’t have to be complicated. A simple notebook or a smartphone app can work wonders. The goal is to build awareness of your body’s responses so you can make informed decisions throughout the day.
Remember, managing diabetes is a journey, and these factors are your guides. Paying attention to them can lead to better control and a healthier life.
Achieving Healthy Blood Sugar
So, you’re looking to get your blood sugar levels in a good place, huh? It sounds like a big deal, and honestly, it is, but it’s totally doable. It’s not just about avoiding the obvious sugary stuff, though that’s a big part of it. We’re talking about a few key things that really make a difference in the long run.
The Role of Healthy Weight
Keeping your weight in check is a pretty big deal when it comes to blood sugar. If you’re carrying extra pounds, your body might not use insulin as well as it should. This can lead to higher blood sugar levels. It’s not about hitting some super-model number, but finding a weight that feels good and healthy for you. Chatting with a doctor or a dietitian can help you figure out what that looks like and how to get there.
Avoiding Nicotine and Tobacco
This one’s a no-brainer, really. Smoking, vaping, or using any tobacco products makes managing blood sugar way harder. It messes with how your body uses insulin and can even make your blood sugar levels spike. Plus, there are a million other health reasons to ditch it. If you’re struggling to quit, there are tons of resources out there to help you out. It’s a tough habit, but totally worth it for your health.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Look, you don’t have to figure all this out alone. Sometimes, you just need a little help from the pros. Your doctor can give you personalized advice, check your levels, and help you understand what your numbers mean. They can also point you toward dietitians or diabetes educators who can offer more specific tips on eating and lifestyle changes. Getting regular check-ups is a smart move for everyone. It’s about staying on top of things and making sure you’re on the right track for good health.
Here are some general targets, but remember to talk to your doctor about what’s right for you:
- A1C: Aim for 7.0% or less (this shows your average blood sugar over 2-3 months).
- Fasting Blood Glucose: Try to keep it between 4.0 to 7.0 mmol/L.
- Blood Sugar Two Hours After Eating: Aim for 5.0 to 10.0 mmol/L (or 5.0 to 8.0 if you’re not hitting your A1C goals).
Managing your blood sugar isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process. Small, consistent changes add up over time. Everyone has off days, so don’t let it stop your progress. Just get back on track with your next meal or activity. Focus on progress, not perfection.
Remember, making smart food choices, like limiting sugary drinks, is a big part of this journey. You can find more information on how to control blood sugar and make healthier choices.
Keeping It In Check
So, managing your blood sugar isn’t some huge, impossible task. It’s really about making smart choices day-to-day. Think about what you eat, making sure to get some protein and fiber in there to slow things down. Moving your body, even just a walk, makes a difference too. And don’t forget to keep an eye on your levels if you can, so you know what works for you. It might take a little getting used to, but these small steps really add up to keeping you feeling your best.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is blood glucose and why is it important?
Blood glucose, often called blood sugar, is the primary type of sugar that circulates in your bloodstream. Your body gets it from the food you consume, and it acts as your main source of energy. Your body uses a hormone called insulin to help move this sugar from your blood into your cells to be used for energy. Keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range is super important for your overall health, especially for your heart, eyes, and kidneys.
What things can make my blood sugar go up or down?
Lots of things can affect your blood sugar! What you eat and how much you eat are big ones. Being active or not being active plays a role too. Even stress, not getting enough sleep, and certain illnesses can make your blood sugar levels change. It’s like a balancing act throughout the day.
How can I keep my blood sugar steady?
You can help keep your blood sugar steady by making smart food choices. Eating foods with protein and fiber can slow down how quickly sugar enters your bloodstream. Balancing your meals with a mix of healthy foods, like vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is key. Also, paying attention to how much you eat is important.
Does exercise really help with blood sugar?
Absolutely! When you exercise, your muscles use up blood sugar for energy, which helps lower your levels. Plus, regular activity helps your body use insulin more effectively. Even a brisk walk can make a difference, and more intense workouts can have a longer-lasting effect.
What’s the deal with carbs and blood sugar?
Carbohydrates, or carbs, are found in foods like bread, pasta, and fruits, and they do make your blood sugar rise after you eat them. But you don’t have to cut them out completely! The trick is to choose the right kinds of carbs, like whole grains which have fiber, and to eat them in balanced portions with protein and healthy fats. It helps slow down how fast the sugar gets into your blood.
Besides food and exercise, what else can I do?
Great question! Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is helpful. It’s also wise to cut back on sugary drinks like soda and juice, and to limit alcohol. Making sure you eat meals around the same time each day and managing your weight are also big factors in keeping your blood sugar in a healthy zone.
for further advice on health and well-being consult our website: https://familytricks.org